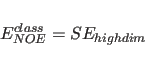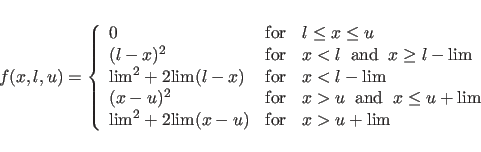| bit | Xplor-NIH | VMD-XPLOR |
|---|
|
| Xplor-NIH home Documentation |
Next: Setup of Distance Restraints Up: Choice of Restraining Functions Previous: 3D NOE-NOE Function
High dimensional Function
For POTEntial=HIGH, a restraining function for stereospecifically assignable proton pairs is employed (Habazettl et al., 1990). This is useful for resolved but unassigned peaks involving methylene protons. The restraining function is given bywhere
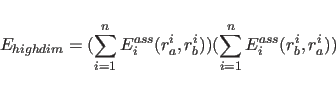 |
(20.18) |
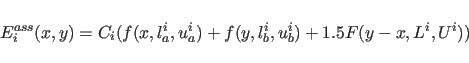 |
(20.19) |

...
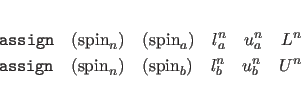
where the
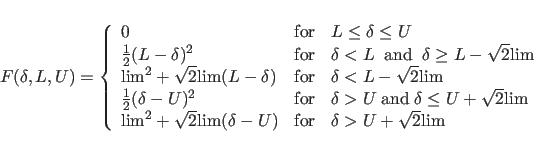
where lim is set internally to 0.1. Xplor-NIH 2025-11-07