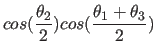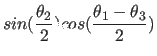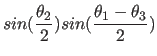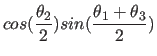| bit | Xplor-NIH | VMD-XPLOR |
|---|
|
| Xplor-NIH home Documentation |
Next: Symbols Up: X-PLOR Language Previous: Three-dimensional Vectors
3 3 Matrices
3 Matrices
The matrix construct allows one to specify a 3 matrix
matrix :==
:==-
- AXIS
 vector
vector
 real
real
- specifies input through
the axis vector and the rotation angle
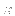 .
.
- EULEr
 vector
vector
- specifies input through the
Eulerian angles
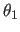 ,
,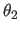 ,
,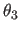 .
.
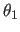 is the rotation around the z axis,
is the rotation around the z axis,
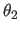 around the new x axis, and
around the new x axis, and 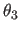 around
the new z axis.
around
the new z axis.
- LATTman
 vector
vector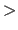
- specifies input
through Lattman's angles
(
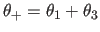 ,
, 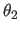 ,
,
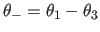 ).
).
- MATRix
 vector
vector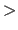
 vector
vector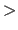
 vector
vector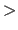
- specifies direct input of the matrix by three 3d-vectors.
- QUATernions
-
 real
real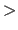
 real
real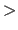
 real
real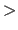
 real
real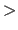 specifies quaternions
specifies quaternions 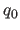 ,
,
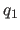 ,
, 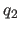 ,
, 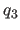 , which are defined as
, which are defined as
with the constraint
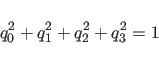
(2.2) - SPHErical
 vector
vector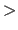
- specifies input through
spherical polar angles
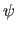 ,
, 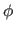 ,
, 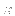 .
.
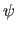 and
and 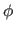 specify the rotation axis.
specify the rotation axis.
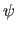 is the inclination versus the y-axis;
is the inclination versus the y-axis; 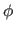 is
the azimuthal angle,
i.e., the angle between the x-axis and the
projection of the axis into the x,z plane; and
is
the azimuthal angle,
i.e., the angle between the x-axis and the
projection of the axis into the x,z plane; and 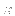 is the rotation around the rotation axis.
is the rotation around the rotation axis.
- AXIS
In the following example, a rotation matrix is specified by
a rotation axis (2,3,4) and a rotation angle (40![]() ) around
the axis (counterclockwise rotation):
) around
the axis (counterclockwise rotation):
AXIS=( 2, 3, 4 ) 40.
In the next example, a matrix is specified by direct input:
MATRix=( 1. 3. 5. )
( 4. 2. 1. )
( 2. 1. 8. )
The last example shows how to specify a rotation matrix by
using the Eulerian angles ![]() ,
,![]() ,
,![]() :
:
EULEr=( 30. 40. 120. )
Xplor-NIH 2025-11-07